C Read Text File Line by Line
In this article, we are going to bear witness you how to read and write to a file in the C++ programming language by using several examples. To empathise C++ file operations like read and write, nosotros must first sympathize the concept of a stream in C++.
What is a Stream?
A stream is only a catamenia of data or characters. There are two types of streams: input streams and output streams. An input stream is used to read the data from an external input device such as a keyboard, while an output stream is used to write data to the external output device such as a monitor. A file can be considered as both an input and output source.
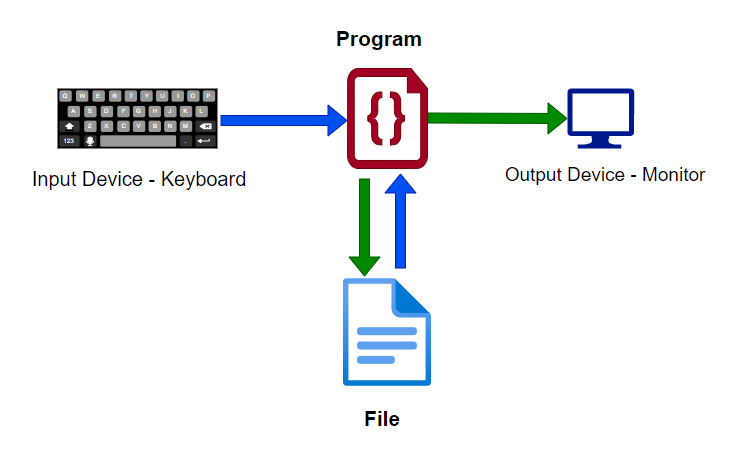
In C++, we use a stream to send or to receive data to or from an external source.
We can use congenital-in classes to admission an input/output stream, i.e., "ios".
Hither is the stream class hierarchy of the C++ programming language:
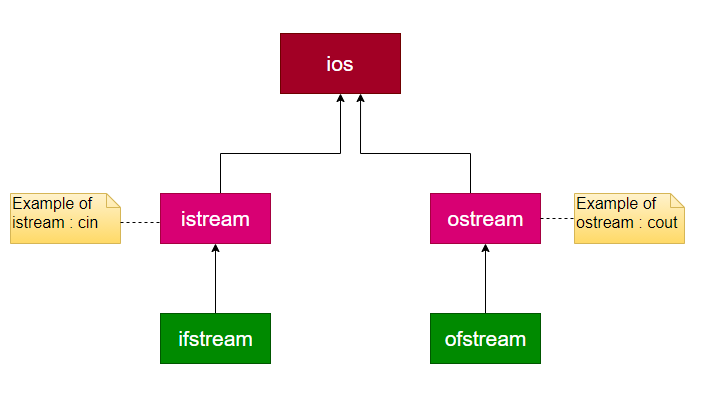
The "cin" and "cout" objects are used to read the information from the keyboard and to brandish the output on the monitor, respectively. In addition, "ifstream," which stands for "input file stream," is used to read a stream of data from a file, and "ofstream," which stands for "output file stream," is used to write a stream of data to a file.
The "iostram.h" file contains all the required standard input/output stream classes in the C++ programming linguistic communication.
Examples
At present that you lot understand the nuts of streams, we volition discuss the following examples to help you lot to ameliorate empathize file operations in C++:
- Example ane: Open and Close a File
- Instance 2: Write to a File
- Example three: Read from a File
- Example 4: Read and Write to a File
- Example 5: Read and Write to a Binary File
Example ane: Open up and Close a File
In this example plan, nosotros will demonstrate how to open/create a file and how to close the file in C++. As you can encounter in the below programme, nosotros have included the library required for file operations.
To open and close a file, we need an object of ofstream. So, to read or write to a file, we take to open the file. We accept included the fstream header file at line number-i so that we can admission ofstream class.
We have declared a myFile_Handler as an object of ofstream within the chief function. We can then use the open() office to create an empty file and the shut() function to close the file.
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
ofstream myFile_Handler;
// File Open up
myFile_Handler.open up ( "File_1.txt" ) ;
// File Shut
myFile_Handler.close ( ) ;
return 0 ;
}
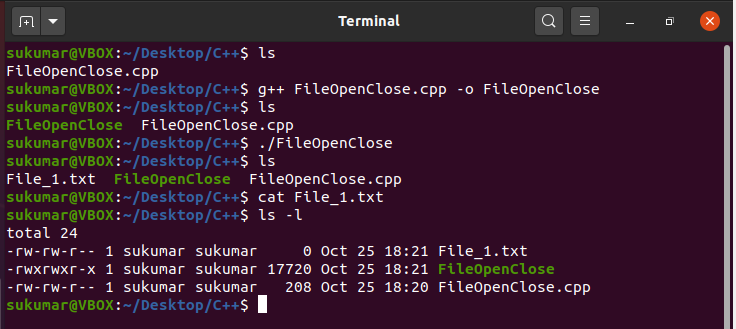
Now, we will compile the programme and examine the output. Every bit you tin can see in the output window below, the "File_1.txt" file was created after executing the programme. The size of the file is zippo since we take not written any content in the file.
Example 2: Write to a File
In the previous example programme, we showed you how to open up a file and how to shut the file. Now, we will show you how to write something in a file.
We can write to a file using the stream insertion operator, i.e., "<<". In this program, nosotros have used the file handler and insertion operator to write two lines in the file. The insertion operator ("<<") indicates that we are inserting the string into the output file stream object.
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int master( )
{
ofstream myFile_Handler;
// File Open
myFile_Handler.open ( "File_1.txt" ) ;
// Write to the file
myFile_Handler << "This is a sample examination File. " << endl;
myFile_Handler << "This is the 2nd line of the file. " << endl;
// File Close
myFile_Handler.shut ( ) ;
return 0 ;
}
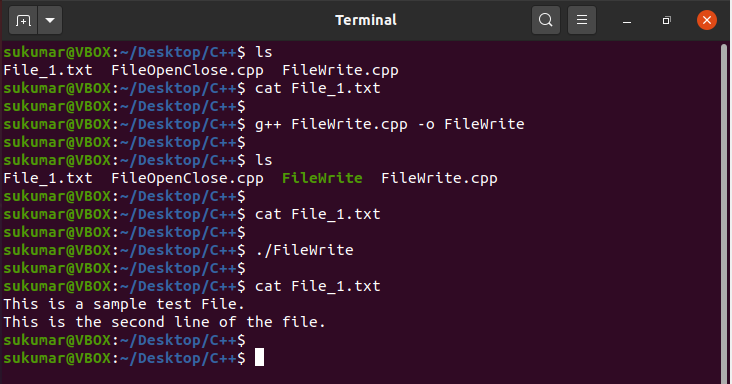
At present, we volition compile the above programme and execute it. As you can see below, we take successfully written to the file File_1.txt.
Example iii: Read from a File
In the previous examples, we showed you lot how to write content to a file. At present, allow's read the content from the file that nosotros created in Example-2 and display the content on the standard output device, i.due east., the monitor.
Nosotros use the getline() role to read the complete line from the file and then "cout" to print the line on the monitor.
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cord>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
ifstream myFile_Handler;
string myLine;
// File Open in the Read Mode
myFile_Handler.open ( "File_1.txt" ) ;
if (myFile_Handler.is_open ( ) )
{
// Go on reading the file
while (getline(myFile_Handler, myLine) )
{
// print the line on the standard output
cout << myLine << endl;
}
// File Close
myFile_Handler.close ( ) ;
}
else
{
cout << "Unable to open the file!" ;
}
return 0 ;
}
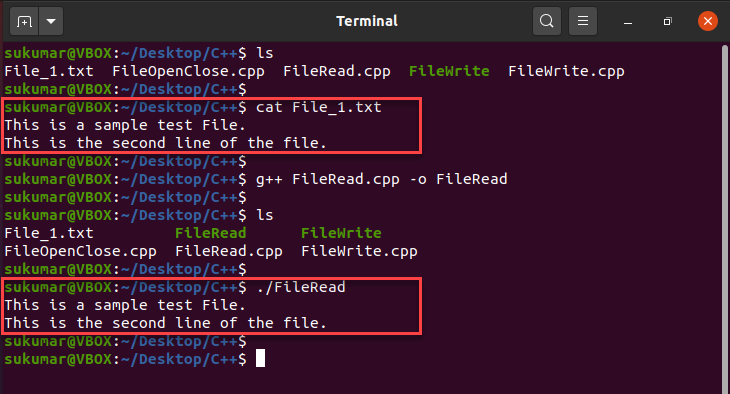
Now, we will impress the content of File_1.txt using the following control: cat File_1.txt. Once nosotros compile and execute the programme, it is clear that the output matches the content of the file. Therefore, nosotros have successfully read the file and printed the content of the file to the monitor.
Case iv: Read and Write to a File
So far, nosotros take showed y'all how to open up, read, write, and shut a file. In C++, we can likewise read and write to a file at the same time. To both read and write to a file, we take to get an fstream object and open the file in "ios::in" and "ios::out" way.
In this example, we first write some content to the file. And then, we read the data from the file and print information technology to the monitor.
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
fstream myFile_Handler;
string myLine;
// File Open
myFile_Handler.open ( "File_1.txt", ios:: in | ios:: out ) ;
// Check if the file has opened
if ( !myFile_Handler)
{
cout << "File did not open up!" ;
get out ( ane ) ;
}
// Write to the file
myFile_Handler << "1. This is another sample test File. " << endl;
myFile_Handler << "2. This is the second line of the file. " << endl;
myFile_Handler.seekg (ios:: beg ) ;
// Read the File
if (myFile_Handler.is_open ( ) )
{
// Go along reading the file
while ( getline(myFile_Handler, myLine) )
{
// print the line on the standard output
cout << myLine << endl;
}
// File Shut
myFile_Handler.close ( ) ;
}
else
{
cout << "Unable to open up the file!" ;
}
myFile_Handler.shut ( ) ;
return 0 ;
}
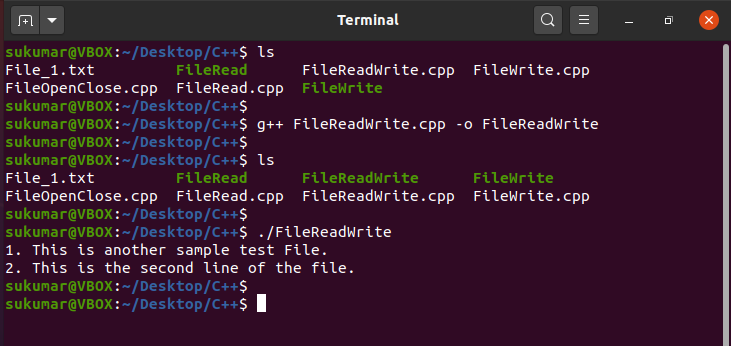
Now, nosotros will compile and execute the plan.
Case 5: Read and Write to a Binary File
In this example, we are going to declare a class and so write the object to a binary file. To simplify this instance, we have alleged the Employee class with a public variable emp_id. So, we will read the binary file and print the output to the monitor.
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
course Employee
{
public :
int emp_id;
} ;
int principal( )
{
ofstream binOutFile_Handler;
ifstream binInFile_Handler;
Employee empObj_W, empObj_R;
// File Open
binOutFile_Handler.open ( "Employee.dat", ios:: out | ios:: binary ) ;
// Check if the file has opened
if ( !binOutFile_Handler)
{
cout << "File did not open!" ;
exit ( i ) ;
}
// Initialize empObj_W
empObj_W.emp_id = 1512 ;
// Write to the file
binOutFile_Handler.write ( ( char * ) &empObj_W, sizeof (Employee) ) ;
binOutFile_Handler.close ( ) ;
if ( !binOutFile_Handler.good ( ) )
{
cout << "Error occured during writing the binary file!" << endl;
leave ( 2 ) ;
}
// Now, allow'due south read the employee.dat file
binInFile_Handler.open up ( "Employee.dat", ios:: in | ios:: binary ) ;
// Check if the file has opened
if ( !binInFile_Handler)
{
cout << "File did not open up!" ;
exit ( 3 ) ;
}
// Read the content of the binary file
binInFile_Handler.read ( ( char * ) &empObj_R, sizeof (Employee) ) ;
binInFile_Handler.close ( ) ;
if ( !binInFile_Handler.adept ( ) )
{
cout << "Error occured during reading the binary file!" << endl;
go out ( four ) ;
}
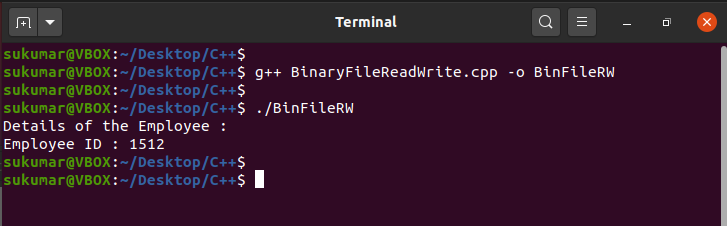
// Print the output of empObj_R
cout << "Details of the Employee : " << endl;
cout << "Employee ID : " << empObj_R.emp_id << endl;
return 0 ;
}
Conclusion
Files are mainly used to store the data, and they play an important role in real-world programming. In this article, we showed you how to use various file operations with the C++ programming language by working through several examples. Furthermore, we showed you how to read and write data into both text files and binary files.
Source: https://linuxhint.com/cplusplus_read_write/
0 Response to "C Read Text File Line by Line"
Post a Comment